In robotics, “Wizard of Oz” (WoZ) experiments refer to a research setup in which a human operator covertly controls a robot, creating the illusion that the robot is autonomous.
This experimental design, inspired by the man behind the curtain in the classic story “The Wizard of Oz,” allows researchers to simulate the behavior of sophisticated autonomous robots without the need for complex programming or complete autonomous capabilities. This methodology is particularly valuable in early-stage development and human-robot interaction (HRI) studies, where the focus is on understanding human responses to robotic behaviors.
Why WoZ Matters:
- Rapid Prototyping: WoZ enables quick iterations of robotic behaviors without the need for fully developing the underlying autonomous systems.
- Human-centered design: Allows researchers to gather human feedback on robot design and behavior in a realistic setting, ensuring that the end product is user-friendly.
- Cost-Efficiency: By simulating autonomy, researchers can avoid the high costs associated with developing and testing actual autonomous capabilities in the prototype phase.
In the realm of Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), the applications of WoZ experiments are multifaceted and invaluable. Researchers leverage WoZ to delve into behavior experimentation, analyzing human responses to a robot’s myriad actions, gestures, and communication methods. It’s instrumental in social robotics for probing the intricate nuances of human-robot social exchanges, unfettered by the constraints of present-day AI.
The technique also facilitates emotion recognition, allowing robots to interpret and respond to human emotions adeptly while gauging cognitive load to tailor interactions, particularly in educational contexts. Moreover, WoZ experiments are pivotal in exploring ethical decision-making, which is essential for fostering trust and ensuring that robots behave in a manner that aligns with human ethical standards. Lastly, these experiments are crucial for perfecting human-robot teamwork, ensuring that collaborative efforts are smooth and effective.
Performing WoZ experiments requires a set of tools that enable the human operator to control the robot seamlessly and unobtrusively.
The right application should provide the following:
- Intuitive Controls: Easy-to-use interfaces for the operator to manage the robot’s actions without delay or complications.
- Versatility: The ability to simulate a wide range of robotic behaviors and responses to fit various research scenarios.
- Real-Time Feedback: Systems that allow the operator to receive immediate feedback from the robot and the environment to adjust the control actions accordingly.
For instance:

- Activation Buttons: Allow operators to trigger predefined robot gestures and behaviors, facilitating smooth and natural human-robot interactions.
- Text Sender: This feature can be connected to any input stream of the robot.
For instance, a text-to-speech ROS node enables the robot to communicate with users using natural language. - Virtual Joysticks: For precise control over robot movement, virtual joysticks give the Wizard the ability to navigate the robot through complex environments in a way that would be perceived as natural by humans.

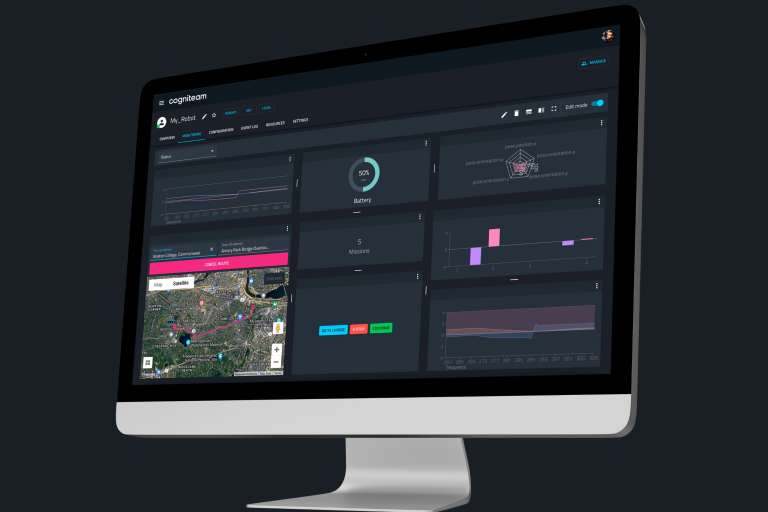
Monitoring and Teleoperation in the Cogniteam Cloud Platform
The following video depicts an HRI experiment. The Wizard switches between an autonomous mode implemented by the HRI Toolkit and a controlled mode. In this experiment, we use the Cogniteam Cloud Platform, which is equipped with the necessary tools to create realistic and sophisticated WoZ experiments. The Wizard quickly and easily switches between autonomous and controlled behaviors, accelerating the development of robots that are intuitive and effective in interacting with humans.
“Wizard of Oz” experimentation is a cornerstone in the field of robotics, especially in the realm of HRI. It allows you to explore the nuances of human-robot interaction without the immediate need for complete autonomous technology. The ability to conduct these experiments effectively hinges on the availability of robust platforms, which provide a suite of features for seamless teleoperation and monitoring.
By leveraging such platforms, robotics companies can refine their technologies to achieve higher levels of sophistication and user satisfaction in their human interactions. As we progress into a future where robots become increasingly integrated into our daily lives, the value of WoZ experiments and the platforms that support them will only continue to grow.

Dr. Eliahu Khalastchi,
Research Scientist